Which Type of Visualization Tool Can Be Very Helpful When a Data Set Contains Location Data?
Yous can apply a PivotTable to summarize, analyze, explore, and nowadays summary information. PivotCharts complement PivotTables by adding visualizations to the summary data in a PivotTable, and let y'all to easily see comparisons, patterns, and trends. Both PivotTables and PivotCharts enable you to make informed decisions about critical data in your enterprise. You can also connect to external data sources such as SQL Server tables, SQL Server Assay Services cubes, Azure Marketplace, Office Information Connection (.odc) files, XML files, Access databases, and text files to create PivotTables, or apply existing PivotTables to create new tables.
Annotation:The screen shots in this commodity were taken in Excel 2016. If you have a different version your view might be slightly different, just unless otherwise noted, the functionality is the same.
Almost PivotTables
A PivotTable is an interactive way to speedily summarize large amounts of data. You can apply a PivotTable to analyze numerical data in particular, and respond unanticipated questions about your data. A PivotTable is specially designed for:
-
Querying large amounts of data in many user-friendly ways.
-
Subtotaling and aggregating numeric data, summarizing data by categories and subcategories, and creating custom calculations and formulas.
-
Expanding and collapsing levels of data to focus your results, and drilling down to details from the summary data for areas of interest to you.
-
Moving rows to columns or columns to rows (or "pivoting") to encounter different summaries of the source data.
-
Filtering, sorting, grouping, and conditionally formatting the most useful and interesting subset of data enabling you to focus on just the data you want.
-
Presenting curtailed, attractive, and annotated online or printed reports.
For case, here's a uncomplicated list of household expenses on the left, and a PivotTable based on the list to the right:
| Household expense information | Respective PivotTable |
| | |
For more than information, come across Create a PivotTable to clarify worksheet information.
After you create a PivotTable by selecting its information source, arranging fields in the PivotTable Field List, and choosing an initial layout, you can perform the following tasks every bit you work with a PivotTable:
Explore the data past doing the following:
-
Expand and plummet data, and evidence the underlying details that pertain to the values.
-
Sort, filter, and group fields and items.
-
Change summary functions, and add together custom calculations and formulas.
Change the form layout and field arrangement by doing the following:
-
Modify the PivotTable grade: Compact, Outline, or Tabular.
-
Add, rearrange, and remove fields.
-
Change the guild of fields or items.
Change the layout of columns, rows, and subtotals by doing the post-obit:
-
Turn cavalcade and row field headers on or off, or display or hide blank lines.
-
Brandish subtotals in a higher place or below their rows.
-
Adapt cavalcade widths on refresh.
-
Move a column field to the row area or a row field to the column area.
-
Merge or unmerge cells for outer row and column items.
Change the display of blanks and errors by doing the following:
-
Change how errors and empty cells are displayed.
-
Alter how items and labels without data are shown.
-
Brandish or hide blank rows
Change the format by doing the post-obit:
-
Manually and conditionally format cells and ranges.
-
Change the overall PivotTable format style.
-
Change the number format for fields.
-
Include OLAP Server formatting.
For more information, see Design the layout and format of a PivotTable.
PivotCharts provide graphical representations of the data in their associated PivotTables. PivotCharts are too interactive. When yous create a PivotChart, the PivotChart Filter Pane appears. You can use this filter pane to sort and filter the PivotChart's underlying data. Changes that you lot make to the layout and data in an associated PivotTable are immediately reflected in the layout and information in the PivotChart and vice versa.
PivotCharts brandish data series, categories, information markers, and axes but every bit standard charts exercise. You tin also change the chart type and other options such every bit the titles, the legend placement, the data labels, the chart location, and and so on.
Here's a PivotChart based on the PivotTable example above.
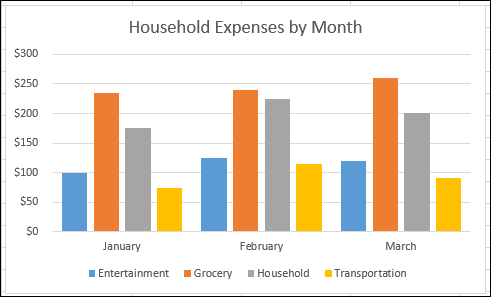
For more data, run across Create a PivotChart.
If you lot are familiar with standard charts, you will detect that most operations are the same in PivotCharts. Withal, there are some differences:
Row/Cavalcade orientation Unlike a standard nautical chart, you cannot switch the row/column orientation of a PivotChart by using the Select Data Source dialog box. Instead, you can pivot the Row and Cavalcade labels of the associated PivotTable to reach the same effect.
Chart types You can alter a PivotChart to any chart blazon except an xy (scatter), stock, or bubble chart.
Source data Standard charts are linked straight to worksheet cells, while PivotCharts are based on their associated PivotTable'southward data source. Unlike a standard chart, you cannot alter the chart information range in a PivotChart's Select Data Source dialog box.
Formatting Most formatting—including chart elements that you add, layout, and style—is preserved when y'all refresh a PivotChart. Even so, trendlines, data labels, error bars, and other changes to data sets are not preserved. Standard charts practice non lose this formatting once it is applied.
Although you cannot directly resize the data labels in a PivotChart, you can increase the text font size to finer resize the labels.
You can use data from a Excel worksheet as the basis for a PivotTable or PivotChart. The information should be in listing format, with cavalcade labels in the commencement row, which Excel volition use for Field Names. Each jail cell in subsequent rows should comprise data appropriate to its cavalcade heading, and y'all shouldn't mix data types in the aforementioned column. For case, you shouldn't mix currency values and dates in the same column. Additionally, there shouldn't be any blank rows or columns inside the data range.
Excel tables Excel tables are already in list format and are adept candidates for PivotTable source data. When you refresh the PivotTable, new and updated data from the Excel tabular array is automatically included in the refresh performance.
Using a dynamic named range To make a PivotTable easier to update, you can create a dynamic named range, and use that proper name every bit the PivotTable's data source. If the named range expands to include more data, refreshing the PivotTable will include the new information.
Including totals Excel automatically creates subtotals and m totals in a PivotTable. If the source data contains automatic subtotals and 1000 totals that yous created by using the Subtotals command in the Outline group on the Data tab, use that same command to remove the subtotals and chiliad totals earlier you create the PivotTable.
You tin can retrieve information from an external data source such every bit a database, an Online Belittling Processing (OLAP) cube, or a text file. For example, you might maintain a database of sales records you want to summarize and analyze.
Role Information Connection files If you utilize an Office Data Connection (ODC) file (.odc) to recall external information for a PivotTable, y'all can input the data straight into a PivotTable. We recommend that yous retrieve external data for your reports by using ODC files.
OLAP source data When you retrieve source data from an OLAP database or a cube file, the data is returned to Excel only as a PivotTable or a PivotTable that has been converted to worksheet functions. For more than information, see Convert PivotTable cells to worksheet formulas.
Non-OLAP source data This is the underlying data for a PivotTable or a PivotChart that comes from a source other than an OLAP database. For instance, data from relational databases or text files.
For more information, encounter Create a PivotTable with an external data source.
The PivotTable cache Each time that you create a new PivotTable or PivotChart, Excel stores a copy of the data for the report in retentivity, and saves this storage area as part of the workbook file - this is chosen the PivotTable cache. Each new PivotTable requires boosted memory and disk space. However, when yous utilize an existing PivotTable as the source for a new one in the same workbook, both share the aforementioned cache. Considering you reuse the enshroud, the workbook size is reduced and less data is kept in memory.
Location requirements To apply ane PivotTable as the source for another, both must be in the same workbook. If the source PivotTable is in a different workbook, copy the source to the workbook location where you want the new 1 to appear. PivotTables and PivotCharts in different workbooks are separate, each with its own copy of the data in memory and in the workbooks.
Changes touch on both PivotTables When you refresh the data in the new PivotTable, Excel likewise updates the data in the source PivotTable, and vice versa. When you group or ungroup items, or create calculated fields or calculated items in i, both are affected. If yous need to have a PivotTable that'due south independent of another one, then you tin can create a new ane based on the original data source, instead of copying the original PivotTable. Merely be mindful of the potential memory implications of doing this likewise oft.
PivotCharts You can base a new PivotTable or PivotChart on another PivotTable, simply yous cannot base a new PivotChart straight on some other PivotChart. Changes to a PivotChart affect the associated PivotTable, and vice versa.
Changes in the source data can event in different data being available for analysis. For instance, yous may want to conveniently switch from a test database to a product database. You lot can update a PivotTable or a PivotChart with new data that is like to the original information connection information past redefining the source data. If the data is substantially different with many new or additional fields, it may be easier to create a new PivotTable or PivotChart.
Displaying new data brought in by refresh Refreshing a PivotTable can also alter the information that is bachelor for brandish. For PivotTables based on worksheet information, Excel retrieves new fields within the source range or named range that you specified. For reports based on external data, Excel retrieves new data that meets the criteria for the underlying query or information that becomes available in an OLAP cube. You lot tin view whatever new fields in the Field List and add the fields to the report.
Irresolute OLAP cubes that you lot create Reports based on OLAP information always have access to all of the data in the cube. If y'all created an offline cube that contains a subset of the information in a server cube, yous can utilize the Offline OLAP control to alter your cube file so that information technology contains dissimilar information from the server.
Demand more than help?
You lot can always ask an adept in the Excel Tech Customs or get back up in the Answers community.
Run into Also
Create a PivotTable to analyze worksheet data
Create a PivotChart
PivotTable options
Use PivotTables and other business intelligence tools to clarify your data
Source: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/overview-of-pivottables-and-pivotcharts-527c8fa3-02c0-445a-a2db-7794676bce96
0 Response to "Which Type of Visualization Tool Can Be Very Helpful When a Data Set Contains Location Data?"
إرسال تعليق